View Jobs
You can check the status of the job on the Job History page. Once the job is successfully completed, you will receive an email notification indicating the successful completion of the job. You can download the results by clicking on the respective Job ID and Results links
- Clicking on Job ID in the Job History Page
The Results folder contains the simulation graphs, images, input files, and PDF report. These files include all the data. A sample report with a brief description is attached below for your reference.
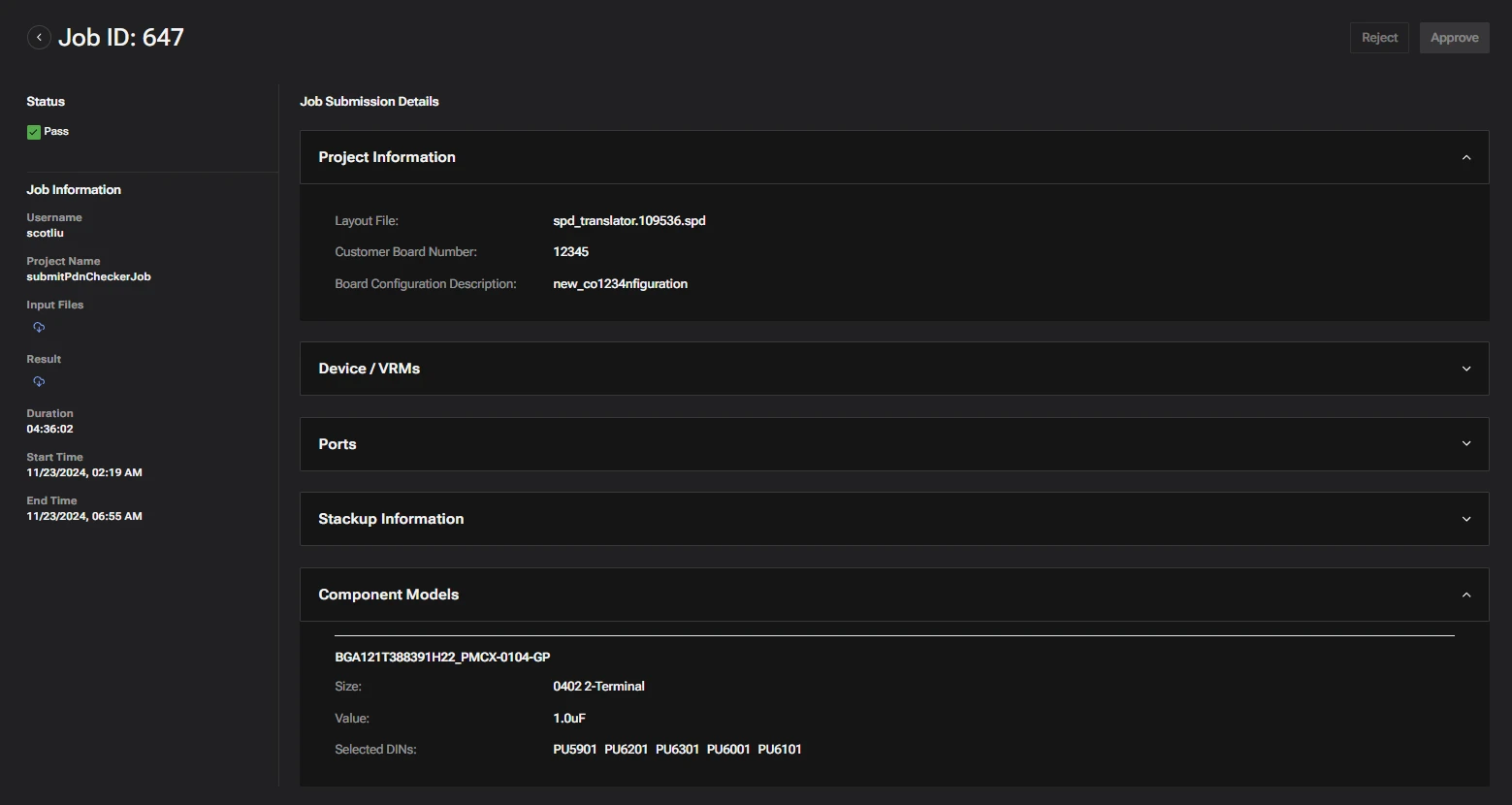
About the Self Impedence Table

- Target Met: Provides an overall verdict of the simulation for a given rail.
- PDN Group: Rail name.
- Port Name: Port under a given rail.
- Max Cross-Z Port: Other port in the PDN group that is causing the highest cross impedance with the port (mentioned in Port Name).
- ZPK1-Result Impedance: Reports the maximum cross impedance in the frequency region of 1 MHz to 5 MHz.
- ZPK1-Target: Provides the target cross impedance at the measured frequency.
- ZPK1-Frequency: Measured frequency where the cross impedance is maximum.
- ZPK2-Result Impedance: Reports the maximum cross impedance in the frequency region of 5 MHz to 24 MHz.
- ZPK2-Target: Provides target impedance at the measured frequency.
- ZPK2-Frequency: Measured frequency at which impedance is maximum.
- 200MHz-Result Impedance: Reports the impedance at 200MHz.
- 200MHz-Target: Impedance target at 200MHz.
- 200MH-Result Inductance: Reports the inductance in pH measured from a slope between 190MHz and 200MHz.
- 200MHz-Target: Inductance target.
Vdrop Table
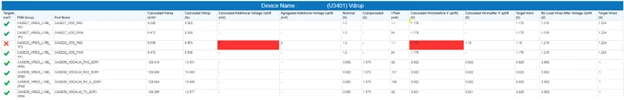
- Target Met: Gives overall verdict of simulation for a given rail
- PDN Group: Rail name
- Port Name: Port under a given rail
- Calculated Vdrop (mV): Evaluated the voltage drop as seen at the load port pins, considering the current taken by all the load ports in the PDN group and the self/transfer resistances extracted from the simulation.
- Calculated Vdrop (%): Voltage drop as a percentage of the nominal voltage of the rail.
- Calculated additional voltage uplift (mV): Additional uplift required at PMIC to meet the Vmin specification.
- Aggregated Additional Voltage Uplift (mV): Maximum of the additional uplift required considering all the ports.
- Nominal (V): PMIC Set Voltage.
- Compensated (V): Estimation of the final voltage after boost seen at the output of regulators (which have a feedback mechanism) to maintain the nominal voltage at the sense tap location. Note that this column will have data only for those ports which are driven by regulators with feedback.
- Ipeak (mA): Peak current taken by the port
- Calculated Vmin (before uplift): Worst case minimum voltage that will be seen at the port, before the PMIC voltage uplift.
- Calculated Vmin (after uplift): Worst case minimum voltage seen at the load port after the PMIC voltage uplift.
- Target Vmin (V): Vmin specification for the load port
- Calculated Vmax (after uplift): Worst case maximum voltage seen at the load port after the PMIC voltage uplift.
- Target Vmax (V): Vmax specification for the load port.
Please refer 80-VT310-90 PDN Voltage Drop Methodology for more details.
VRM Table
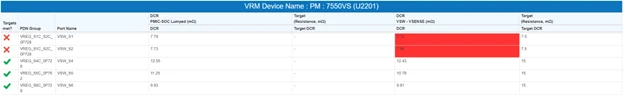
- Target Met: Gives overall verdict of simulation for a given rail
- PDN Group: Rail name
- Port Name: Port under a given rail; it will be the switching pin for SMPS or the voltage output pin in the case of LDO.
- DCR PMIC Lumped-SoC (mOhm): Provides DCR measurement in mOhm between the listed source and the load device for a given port.
- Target: Target resistance for above.
- DCR Vsense-SOC (mOhm): Provides DCR measurement in mOhm between the sense trace tap point on the power net and the load port.